What are Anal Warts?
Definition of Anal Warts
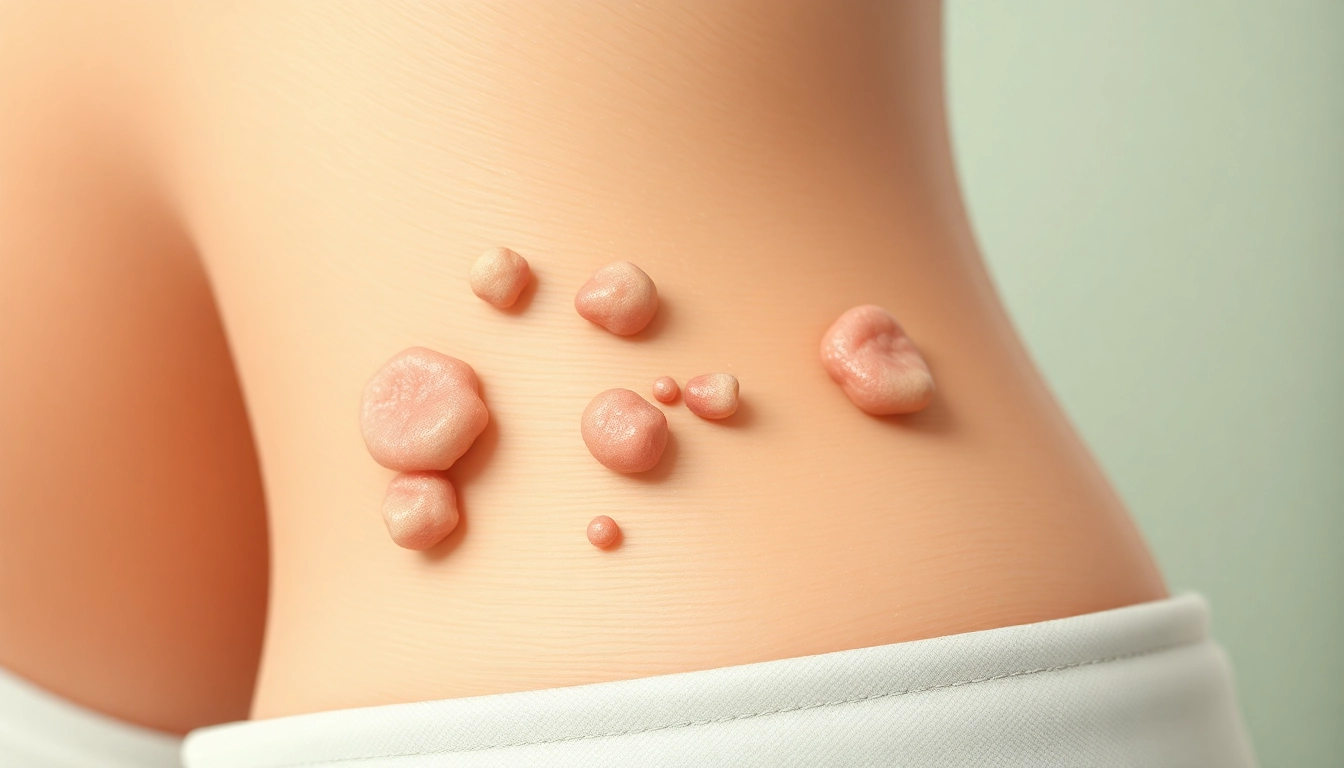
Anal warts, medically known as condyloma acuminata, are benign growths that occur in and around the anal region due to infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). These warts can vary in size from very small to larger clusters resembling a cauliflower. They can appear at or inside the anus and may affect both men and women.
Causes of Anal Warts
The primary cause of anal warts is infection with high-risk strains of the HPV virus, primarily types 6 and 11. These strains are transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact, which often occurs during sexual activity. Other factors that can increase the likelihood of developing anal warts include:
- Multiple sexual partners: Having multiple partners can increase exposure to HPV.
- Immune system suppression: Conditions or medications that weaken the immune system can make it easier for HPV to cause warts.
- Other sexually transmitted infections: Presence of other STIs can increase susceptibility to HPV infection.
Anal warts can affect individuals regardless of sexual orientation or predisposition; however, those who practice unprotected anal intercourse are at a higher risk of contracting HPV.
How Anal Warts Differ from Other Conditions
While anal warts may share features with other anal conditions such as hemorrhoids or anal fissures, they are distinguishable based on several characteristics:
- Appearance: Anal warts appear as raised lesions with a rough or cauliflower-like texture, whereas hemorrhoids are swollen blood vessels.
- Location: Anal warts grow on the skin around the anus and sometimes inside the anal canal, while hemorrhoids are internal or external swellings.
- Symptoms: Anal warts may cause itching or discomfort, whereas hemorrhoids can lead to pain during bowel movements and bleeding.
Symptoms of Anal Warts
Common Physical Symptoms
Anal warts can manifest various physical symptoms, though some individuals may be asymptomatic. Common signs include:
- Itching: Persistent itching around the anal area is one of the most common complaints.
- Bleeding: Bright red blood may appear, especially during bowel movements.
- Visible growths: Warts may appear as small fleshy bumps that can cluster together.
Pain and Discomfort Associated with Anal Warts
While anal warts are generally not painful, their presence can cause discomfort. Larger warts can irritate surrounding skin, leading to a sensation of heaviness or pressure. This discomfort may be exacerbated during bowel movements, potentially causing anxiety about going to the bathroom.
Recognizing Symptoms Early
Early identification of symptoms is crucial for managing anal warts effectively. Individuals should consult a healthcare professional if they notice any abnormal growths or experience discomfort in the anal region. Recognizing these symptoms promptly can lead to timely diagnosis and treatment, reducing potential complications.
Diagnosis of Anal Warts
Clinical Examination for Anal Warts
The diagnosis of anal warts typically begins with a thorough clinical examination. Healthcare providers will visually inspect the anal area for any growths. In some cases, a digital rectal examination may be performed to assess any internal lesions.
Diagnostic Tests for Confirmation
Although a clinical examination is often sufficient to diagnose anal warts, additional tests may be used to confirm HPV infection or rule out other conditions. These can include:
- Pap smear: For women, a Pap test can identify HPV changes in cervical cells, suggesting a potential risk for anal warts.
- Biopsy: In rare cases, a small sample of tissue may be taken for pathological examination to confirm the presence of HPV.
Factors Influencing Diagnosis
Several factors can affect the diagnostic process, including:
- Patient history: A detailed sexual history and previous diagnoses may aid the physician in determining the likelihood of HPV infection.
- Physical examination findings: The size, location, and number of warts can influence the diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Anal Warts
Topical Treatments for Anal Warts
For many patients, topical treatments are the first-line approach for managing anal warts. Options include:
- Podophyllin: A plant-derived cytotoxic agent applied directly to the warts to promote their destruction.
- Imiquimod: A cream that helps stimulate the immune system to fight against HPV.
- Sinecatechins: A botanical ointment that works similarly to promote the resolution of warts.
These treatments require careful application and may take several weeks to demonstrate effects. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions explicitly to minimize side effects.
Surgical Interventions for Severe Cases
In cases where anal warts are extensive, painful, or resistant to topical treatments, surgical options may be indicated. Surgical methods include:
- Excision: Warts can be surgically removed using a scalpel.
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the warts with liquid nitrogen causes them to fall off.
- Laser therapy: A focused beam of light is used to vaporize warts.
The choice of surgical intervention depends on the size, number, and location of the warts, as well as the patient’s overall health status.
Follow-up and Aftercare for Anal Warts
Post-treatment care is essential for optimal recovery. Patients are advised to:
- Monitor for any recurrence of warts.
- Maintain hygiene in the anal region.
- Engage in safe sexual practices to avoid reinfection.
Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider ensure ongoing assessment and management.
Preventing Anal Warts
Preventive Measures Against HPV
While complete prevention of HPV is challenging, certain strategies can significantly reduce the risk of contracting or transmitting the virus:
- Consistent condom use: Although not foolproof, the use of condoms can reduce the likelihood of HPV transmission.
- Limiting the number of sexual partners: Reducing sexual partners minimizes exposure potential.
Safe Practices to Avoid Anal Warts
In addition to injury prevention strategies, certain behaviors can contribute to reducing the risk of developing anal warts. These include:
- Regular STI screenings: Routine testing can help identify HPV and other STIs early on.
- Open communication: Discussing sexual histories and infection risks with partners promotes awareness and caution.
Importance of Vaccination for HPV
The HPV vaccine is one of the most effective preventive measures against anal warts and their associated risks. Vaccination is recommended for preteens, but adults may also benefit. The vaccine provides protection against the most common high-risk HPV strains that lead to warts and potentially more severe complications.
In summary, anal warts are a common concern stemming from HPV infections, but with proper knowledge and proactive measures, their impact can be minimized. Understanding the symptoms, seeking timely diagnosis, employing effective treatments, and adopting preventive strategies can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for those affected.